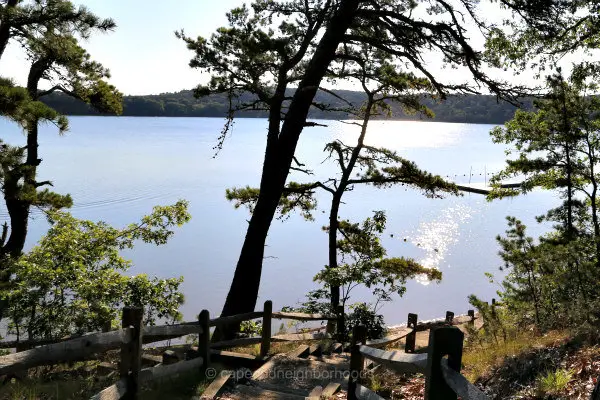
Have you ever come across the term “kettle pond” and wondered what it means? Kettle ponds are more than just bodies of water; they are geological marvels that offer a glimpse into the Earth’s history. In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of kettle ponds, exploring their formation, characteristics, and ecological significance.

Credit: www.wbur.org
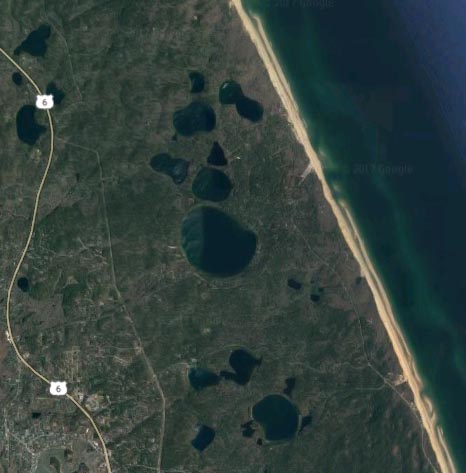
Credit: www.wbur.org
Understanding Kettle Ponds
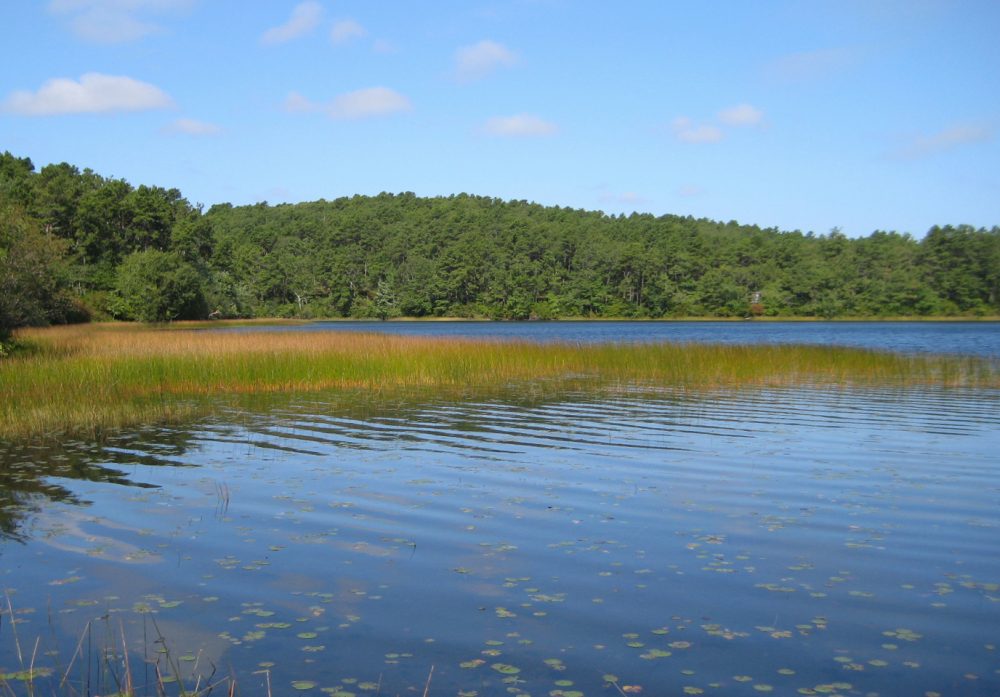
A kettle pond is a small, shallow body of water that forms in a depression on the Earth’s surface. These unique water features are typically found in regions that were once covered by glaciers, such as parts of North America, Europe, and Asia. The formation of kettle ponds is closely tied to the processes of glaciation and deglaciation, which occurred during the last ice age.
Formation Of Kettle Ponds
During the last ice age, massive sheets of ice, known as glaciers, covered vast areas of the Earth’s surface. As these glaciers advanced and retreated, they left behind a variety of landforms, including kettle ponds. The formation of a kettle pond begins with a block of ice that becomes buried in glacial deposits, such as sand and gravel. When the ice eventually melts, it creates a depression in the ground, which is then filled with water, forming a kettle pond.
Characteristics Of Kettle Ponds
Kettle ponds are known for their unique characteristics, which set them apart from other types of water bodies. These features include:
- Shallow Depth: Kettle ponds are typically shallow, with depths ranging from a few feet to several meters.
- Irregular Shape: Due to the manner in which they are formed, kettle ponds often have irregular shapes, with no defined inlet or outlet.
- Clear Water: The water in kettle ponds is often crystal clear, as it is fed by groundwater and precipitation rather than flowing streams.
- Ecological Diversity: Kettle ponds support a wide variety of plant and animal life, making them important habitats for biodiversity.
Ecological Significance of Kettle Ponds
Despite their relatively small size, kettle ponds play a crucial role in the ecosystems where they are found. These unique water bodies provide valuable habitats for a diverse array of plant and animal species. The shallow, clear waters of kettle ponds support the growth of aquatic vegetation, which in turn provides food and shelter for insects, amphibians, and other wildlife.
Kettle ponds also serve as breeding grounds for many species of amphibians, including frogs and salamanders. The absence of predatory fish in kettle ponds allows these amphibians to thrive, contributing to the overall ecological balance of the region.
Preservation and Conservation
Given their ecological importance, it is essential to prioritize the preservation and conservation of kettle ponds. Human activities, such as urban development and agriculture, can have a significant impact on these fragile ecosystems. Efforts to protect kettle ponds may include the establishment of protected areas, monitoring water quality, and implementing measures to prevent pollution and habitat destruction.
Education and awareness also play a crucial role in the conservation of kettle ponds. By educating the public about the ecological significance of these unique water bodies, we can foster a greater appreciation for their value and the need to protect them for future generations.
Exploring Kettle Ponds
If you have the opportunity to visit a region where kettle ponds are found, take the time to explore these natural wonders. Many kettle ponds are accessible via hiking trails or nature reserves, offering a chance to observe the diverse flora and fauna that call these ecosystems home. Remember to tread lightly and respect the delicate balance of these environments to ensure their preservation for years to come.
Conclusion
Kettle ponds are more than just bodies of water; they are windows into the Earth’s history and vital components of our natural world. By understanding and appreciating the formation, characteristics, and ecological significance of kettle ponds, we can work towards their preservation and ensure that these remarkable features continue to enrich our planet for generations to come.





