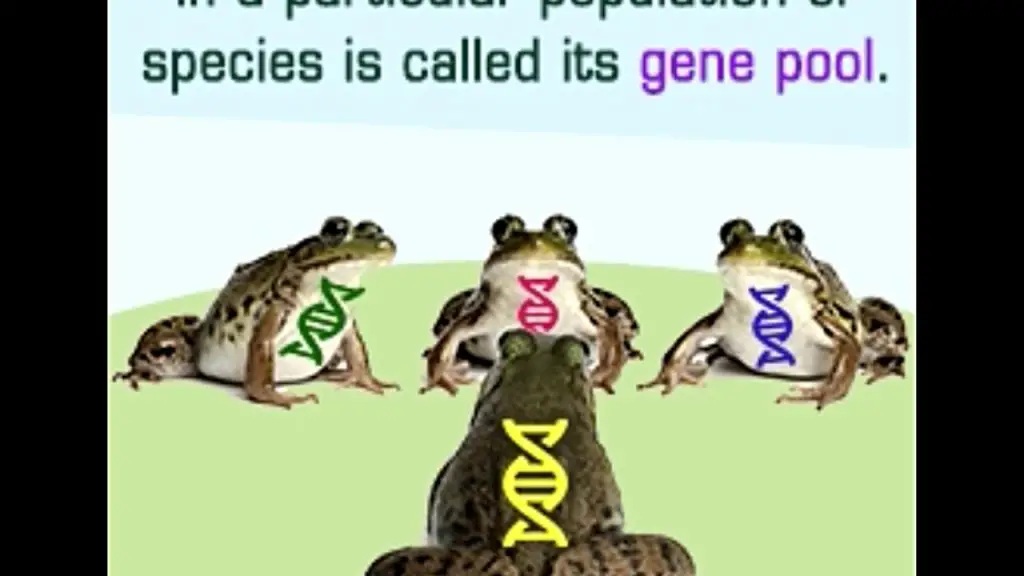
A gene pool refers to the collection of all the genetic information present in a particular population or species. This pool consists of the various genetic variations and combinations that can be inherited by individuals within that population.
It plays a crucial role in determining the overall genetic diversity and potential for adaptation in a species. The gene pool acts as a reservoir from which individuals draw their traits and characteristics, allowing for the continued survival and evolution of the population.
By maintaining a diverse gene pool, populations are more likely to possess the genetic variation necessary to respond to changing environmental conditions and overcome challenges. A healthy gene pool is essential for the long-term viability of a species.
Exploring The Gene Pool
Composition Of Gene Pool
The gene pool refers to the complete set of genes and alleles present in a population. It includes all the genetic information carried by a particular population at a certain time. Every individual contributes to the gene pool through genetic recombination, random mutations, and gene flow.
Factors Influencing Genetic Diversity
1. Mutation rates and patterns.
2. Gene flow or migration of individuals between populations.
3. Natural selection and environmental factors.
4. Genetic drift due to chance events in small populations.
Credit: www.quora.com
Genetic Variation
Genetic variation refers to the differences in the DNA sequences between individuals within a population. These differences result from genetic mutations, genetic recombination, and genetic drift, contributing to the diversity seen within a gene pool. Understanding genetic variation is crucial in comprehending the evolutionary processes shaping life on Earth.
Types Of Genetic Variation
Genetic variation can occur in several forms, including:
- Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs)
- Insertions and deletions of DNA segments
- Copy number variations
Significance In Evolution
Genetic variation plays a pivotal role in the process of evolution. It allows for the emergence of new traits and adaptations, which can either be favored or eliminated by natural selection, influencing the survival and reproduction of organisms.
Role In Adaptation
The gene pool plays a crucial role in adaptation by providing a diverse range of genetic variations that can be selected for in changing environments. This allows species to better adapt and survive in their ever-changing surroundings.
Genetic diversity in a population plays a crucial role in adaptation to changing environments.
Adaptive Traits
Adaptive traits are inherited characteristics that enhance an organism’s ability to survive.
Survival Strategies
Organisms develop unique survival strategies based on their gene pool diversity.
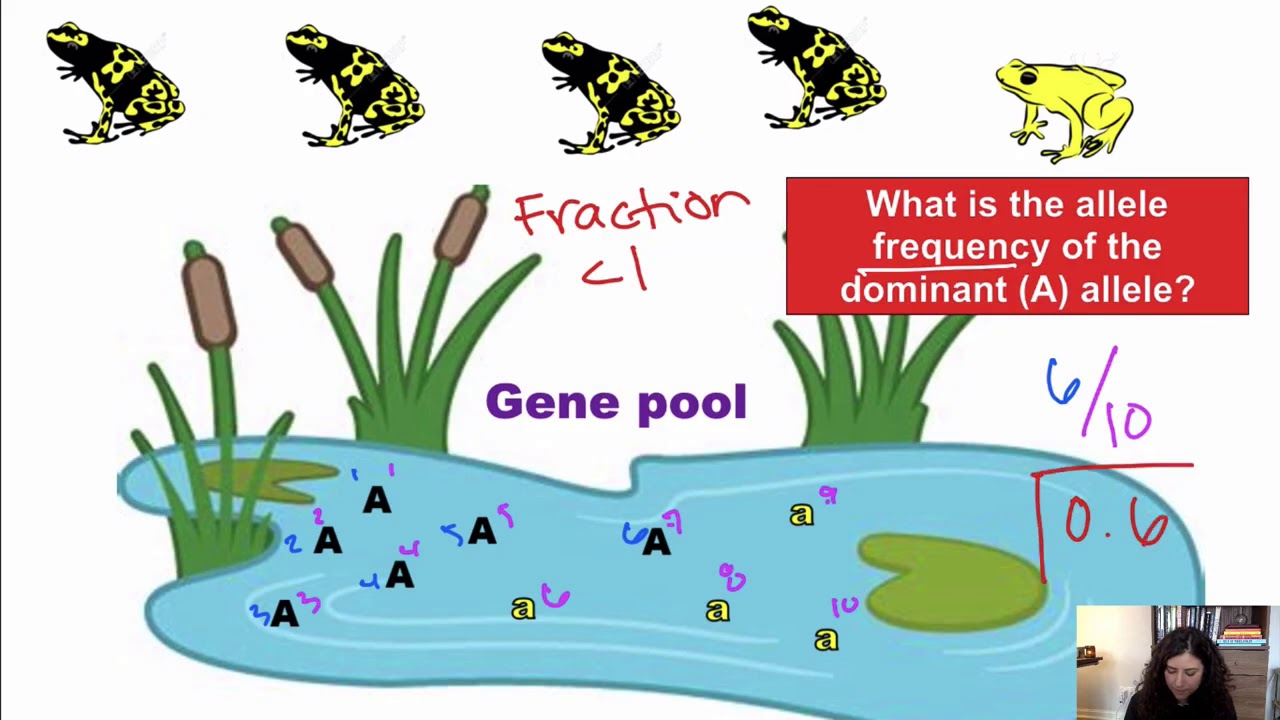
Credit: m.youtube.com
Human Impact
A gene pool refers to the collective genetic information contained within a particular population or species. It represents the total genetic diversity available, which can impact the evolution and adaptation of organisms over time.
The gene pool is a critical aspect of any population, including human populations. However, our increasingly complex and interconnected world has led to a significant impact on human genetic diversity. This impact, driven by factors such as globalization and urbanization, has both positive and negative consequences.
Threats To Genetic Diversity
One of the major threats to human genetic diversity is the loss of traditional lifestyles and cultural practices. As people move away from their ancestral lands and adopt modern ways of living, they often abandon their traditional diets and lifestyles, resulting in a decrease in the variety of genes present in the population. Additionally, the increased intermixing of different ethnic groups has led to the dilution of unique gene pools, further reducing genetic diversity. Another threat to the human gene pool is the extensive use of genetic engineering and the introduction of genetically modified organisms (GMOs). While GMOs can have benefits such as increased crop yield and resistance to pests, they also have the potential to disrupt natural gene flow and introduce new genes into populations. This can lead to unintended consequences and potentially reduce genetic diversity.
Conservation Efforts
In response to the threats faced by human genetic diversity, there have been various conservation efforts put in place. These efforts aim to preserve and protect the diversity of genes present within human populations. One such conservation effort is the establishment of genetic banks and repositories. These facilities collect and store genetic material, such as sperm and egg samples, from individuals representing diverse populations. This ensures that a broad range of genetic material is preserved and available for future use if needed. Additionally, education and awareness campaigns play a crucial role in promoting the importance of genetic diversity. By informing the public about the value of maintaining diverse gene pools, these campaigns encourage individuals and communities to take steps to preserve their unique genetic heritage. Furthermore, fostering cultural pride and identity can also contribute to the conservation of genetic diversity. Celebrating and preserving traditional practices, such as traditional medicine and agricultural techniques, can help communities maintain genetic diversity and prevent the loss of valuable genetic resources. In conclusion, human impact on the gene pool is a complex issue with both positive and negative consequences. While globalization and modernization pose threats to genetic diversity, efforts such as genetic repositories and education campaigns can help preserve and protect the diversity of genes within human populations. By recognizing the value of genetic diversity and taking steps to conserve it, we can ensure a healthier and more resilient future for our species.
Case Studies
In the study of gene pools, case studies play a crucial role in understanding the dynamics of genetic diversity and adaptation. Below are some insightful case studies that shed light on the importance of gene pools in various scenarios.
Endangered Species
Endangered species often face challenges due to limited gene pools, which can lead to inbreeding depression and reduced genetic diversity. Conservation efforts aim to preserve gene pools to ensure the survival of these species.
Population Genetics
Population genetics studies the distribution of genetic variation within and among populations, providing insights into evolutionary processes and genetic adaptation. Understanding gene pools is essential in population genetics research.
Technological Advancements
In the realm of genetics, technological advancements have revolutionized the study and understanding of gene pools. Through the remarkable progress in genomic sequencing and gene editing technologies, scientists have gained unprecedented insight into the complexities of gene pools and their implications for evolution, heredity, and disease.
Genomic Sequencing
Genomic sequencing represents a monumental breakthrough in the exploration of the gene pool. This advanced technology allows researchers to map out the entire genetic makeup of an organism, enabling them to identify unique traits, mutations, and susceptibility to various conditions. By decoding the complete set of genes within a species, scientists can unravel the intricate mechanisms governing genetic diversity and inheritance patterns.
Gene Editing Technologies
Gene editing technologies have opened up previously unimaginable possibilities for manipulating the gene pool. Techniques such as CRISPR (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats) have empowered scientists to precisely alter specific genes within an organism’s genome. This capability holds profound implications for addressing genetic disorders, enhancing agricultural productivity, and preserving biodiversity.
Future Prospects
The future prospects of the gene pool hold great promise for enhancing genetic resilience and ethical considerations. With advances in technology and a deeper understanding of genetics, the potential for positively impacting the gene pool is expanding rapidly. Let’s delve into what the future may hold for the gene pool.
Enhancing Genetic Resilience
Advancements in genetic research and technology offer the potential to enhance the genetic resilience within the gene pool. Researchers are continually exploring ways to identify and address genetic vulnerabilities that may impact the overall health and well-being of a population. This implies that the future may bring breakthroughs in gene editing and therapies that can strengthen genetic resilience and reduce the prevalence of inherited diseases.
Ethical Considerations
As the field of genetics continues to evolve, ethical considerations play a crucial role in shaping the future of the gene pool. It is important to consider the ethical implications of genetic manipulation and ensure that such advancements are used responsibly and with utmost consideration for moral and societal implications. This necessitates ongoing discussions and stringent regulations to govern the ethical use of genetic technology to avoid potential misuse and unintended consequences.

Credit: www.researchgate.net
Conclusion
To sum up, understanding the gene pool is vital for biodiversity and evolution. It’s the collective genetic makeup crucial for species survival and adaptation. By studying this genetic reservoir, scientists can predict traits and disease risks. Appreciating the gene pool’s significance enhances our grasp of the complexity of life forms.