Maintaining the chemical balance in your swimming pool is crucial to ensure clean and safe water for swimmers. By properly calculating and adding the right amount of chemicals, you can prevent algae growth, maintain pH levels, and keep the water crystal clear. In this article, we will guide you through the process of determining how much chemicals to add to your pool.
1. Test the Current Water Chemistry
The first step is to test the current water chemistry of your pool. Use a reliable pool test kit or take a water sample to your local pool supply store for professional testing. The following are the key parameters you should test for:
| Parameter | Ideal Range |
|---|---|
| pH level | 7.4 – 7.6 |
| Total alkalinity | 80 – 120 ppm |
| Calcium hardness | 200 – 400 ppm |
| Free chlorine | 1 – 3 ppm |
2. Determine the Required Chemical Adjustments
Once you have the test results, compare them to the ideal ranges mentioned above. Based on the differences between the actual values and the ideal ranges, you will need to make the necessary chemical adjustments. Here are some common scenarios:
- pH Level: If the pH level is too low, you will need to add a pH increaser (sodium carbonate). If the pH is too high, add a pH reducer (acid).
- Total Alkalinity: If it is too low, you can use sodium bicarbonate to raise it. If it is too high, you will need to decrease it by adding muriatic acid.
- Calcium Hardness: To raise calcium hardness levels, you can add calcium chloride. If it is too high, partially draining and refilling the pool may be necessary.
- Free Chlorine: If the free chlorine level is too low, increase it by adding a chlorine-based shock product. If the level is too high, you might need to let it naturally decrease or use a chlorine reducer.
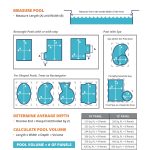
3. Calculate Pool Volume
In order to determine the amount of chemicals needed, you must know the volume of your pool. Use the following formulas to calculate the volume based on its shape:
- Rectangular Pool: Length (ft.) x Width (ft.) x Average Depth (ft.) x 7.5 = Pool Volume in Gallons
- Circular Pool: Radius (ft.) x Radius (ft.) x Average Depth (ft.) x 5.9 = Pool Volume in Gallons
- Oval Pool: Long Radius (ft.) x Short Radius (ft.) x Average Depth (ft.) x 5.9 = Pool Volume in Gallons
Note: Make sure to use consistent units (e.g., feet) in the above calculations.

Credit: poolsbydesignaz.com

Credit: www.astralpool.com.au
4. Chemical Dosage Calculation
Now that you know the pool volume, you can determine the required amount of chemicals using the dosing recommendations provided by the manufacturers on the product labels. Follow their instructions carefully to ensure accurate dosing.
For example, if the chemical bottle recommends adding 1 pound of product per 10,000 gallons of water and your pool volume is 30,000 gallons, you would need to add 3 pounds of that chemical.
5. Add the Chemicals
When adding chemicals to your pool, always follow safety precautions and wear protective gear. Spread the chemicals evenly across the surface of the pool or add them near the return jets to aid in their dispersion. Avoid adding chemicals during windy conditions to prevent inhalation or drift.
It’s important to note that chemical additions should be done gradually. Allow the chemicals to disperse and circulate for a few hours before retesting the water and making further adjustments if needed.
Conclusion
Maintaining the appropriate chemical balance in your pool is essential for the overall health and longevity of your pool system. By regularly testing the water, making the necessary adjustments, and carefully calculating the amount of chemicals to add, you can enjoy a clean and safe swimming environment. Remember, it’s always a good idea to consult a pool professional for personalized advice based on your specific pool conditions.