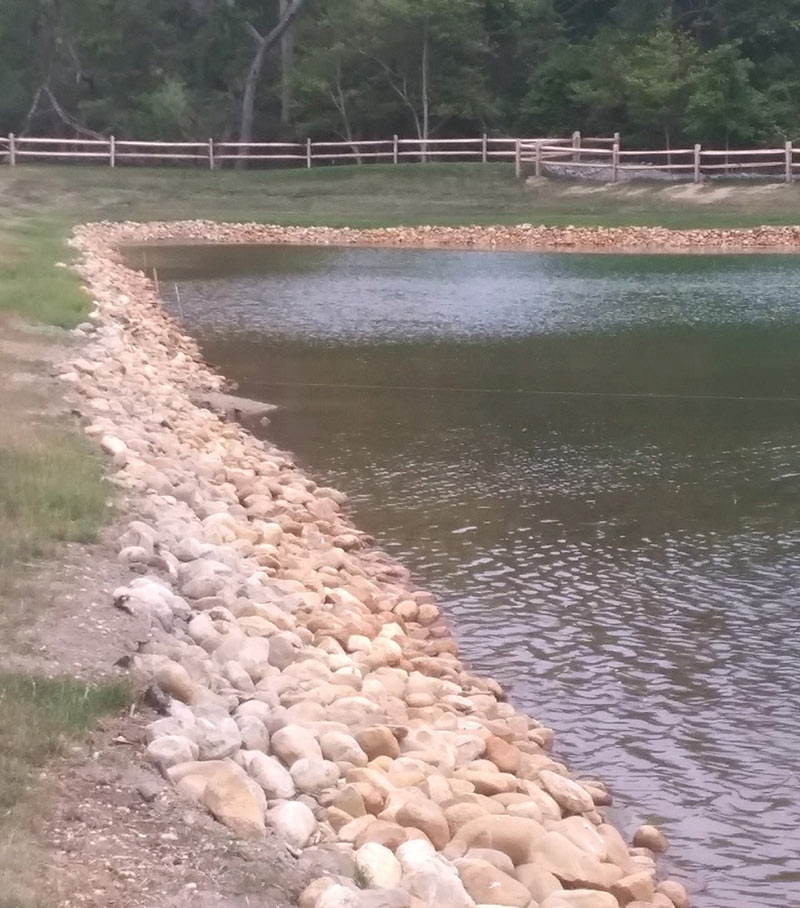
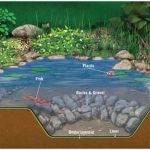
A retention pond’s depth can vary, but its typical depth ranges from 5 to 15 feet. A retention pond, also known as a stormwater or detention pond, is a basin used to collect and temporarily store stormwater runoff.
It is designed to control the release of water into the surrounding environment and prevent flooding. The depth of a retention pond depends on various factors, such as the volume of runoff it needs to accommodate and the site’s topography.
Generally, retention ponds have a depth ranging from 5 to 15 feet. However, the actual depth can vary based on local regulations and design requirements. We will explore the importance of retention ponds, their functionality, and considerations for their design and maintenance. Let’s dive in.
Formation Of Retention Ponds
Formation of Retention Ponds:
Natural Formation
In nature, retention ponds are created through the natural process of depressions forming in the landscape.
Water accumulates in these depressions, creating small bodies of water that serve as retention ponds.
Man-made Construction
Man-made retention ponds are constructed with the purpose of collecting stormwater runoff.
Engineers design these ponds to regulate water flow and prevent flooding in urban areas.
Construction of retention ponds involves excavation of land to create a basin that can hold water during rain events.
Determining Pond Depth
When designing a retention pond, knowing the depth required is crucial for its effectiveness. Proper depth ensures the pond can hold sufficient water to manage runoff during storms.
Technological Tools
Modern technology offers efficient ways to measure pond depth. Here are some technological tools commonly used:
- Laser Leveling Systems
- Depth Sounders
- GPS Mapping
Manual Measurement Techniques
While technological tools are accurate, manual techniques are also effective in determining pond depth:
- Secchi Disk Method
- Grainy Knob Method
- Direct Measurement
Ecological Significance
The retention pond’s ecological significance lies in its vital role in water conservation and its impact on wildlife habitat. These ecological aspects are crucial for maintaining the balance of the ecosystem and preserving natural environments.
Role In Water Conservation
Retention ponds play a critical role in water conservation by serving as a natural filtration system. They act as a reservoir for stormwater, allowing sediment and pollutants to settle at the bottom, preventing them from flowing into natural water bodies.
The pond’s capacity to retain water also helps in replenishing groundwater reserves, contributing to the sustainable management of water resources.
Impact On Wildlife Habitat
Retention ponds provide a diverse and dynamic habitat for various wildlife species. The water body sustains aquatic life such as fish, frogs, and insects, while the surrounding vegetation offers nesting grounds and shelter for birds and small mammals.
The fluctuating water levels in retention ponds create an ever-changing environment, which supports a rich biodiversity of flora and fauna. Additionally, the vegetation growth around the pond provides food and shelter for a wide range of wildlife species.

Credit: www.dirtwirx.com
Structural Considerations
When it comes to the construction of a retention pond, various structural considerations need to be taken into account. These considerations include design and engineering aspects as well as maintenance and safety measures.
Design And Engineering Aspects
The design and engineering aspects of a retention pond are vital to ensuring its effectiveness and longevity. Before constructing a retention pond, a comprehensive analysis of the site is conducted to determine the optimal size and depth needed to accommodate the intended purpose.
The depth of a retention pond will depend on several factors, including the anticipated volume of stormwater runoff, the soil composition of the area, and local regulations. It is crucial to consider the capacity of the pond to prevent overflow during heavy rainfall and provide sufficient storage for water retention.
To optimize water holding capacity, retention ponds are typically designed with slopes that gradually decrease towards the center. This design helps to minimize erosion and maintain stability. In addition, the pond’s shape and dimension should be carefully planned to ensure efficient water flow and maximum storage capacity.
Maintenance And Safety Measures
Maintenance and safety measures play a crucial role in the long-term performance of retention ponds. Regular maintenance is essential to keep the pond operational and prevent potential issues that may affect its functionality.
- Inspecting and cleaning the pond regularly to remove debris and sediment buildup.
- Maintaining the vegetation surrounding the pond for erosion control and natural filtration.
- Ensuring proper functioning of the outlet structures and drainage system to prevent flooding.
- Regularly checking and repairing any cracks or damages to the pond liner.
Safety measures should also be implemented to protect both the environment and individuals using the retention pond area.
- Installing fences or barriers around the pond to prevent unauthorized access.
- Posting clear warning signs depicting potential risks and safety instructions.
- Educating nearby residents and stakeholders about the purpose and dangers associated with the retention pond.
By adhering to these maintenance and safety measures, the retention pond can remain functional and safe for its intended purpose for years to come.
Challenges And Solutions
The depth of a retention pond plays a crucial role in its functionality, and various challenges can arise in maintaining the optimal depth. Addressing these challenges requires effective solutions to ensure the retention pond operates efficiently.
Sedimentation And Dredging
Sedimentation, the accumulation of silt and debris, can significantly reduce the depth of a retention pond, leading to decreased capacity and potential flooding issues. Regular dredging is a solution to remove accumulated sediment and restore the pond’s depth and capacity.
Balancing Water Levels
Maintaining appropriate water levels in a retention pond is essential for its effectiveness. Balancing water levels requires proper management of inflow and outflow, as well as consideration of precipitation and evaporation rates to ensure the pond maintains an optimal depth.

Credit: www.researchgate.net
Regulatory Framework
Regulatory Framework:
Government Policies
Local and federal regulations dictate retention pond specifications and depth requirements.
Environmental Compliance
- Retention pond depth must align with environmental protection standards.
- Government agencies monitor pond depth to ensure environmental sustainability.
- Non-compliance with depth regulations can result in penalties and fines.
Future Perspectives
Future Perspectives: The advancement of retention pond management is paving the way for exciting innovations and adaptations to address climate change challenges.
Innovations In Pond Management
Innovations are revolutionizing the maintenance and ecological balance of retention ponds, enhancing their effectiveness in water conservation.
Adapting To Climate Change
With changing environmental conditions, retention ponds are being adapted to mitigate the impact of climate change on water systems.

Credit: www.twincities.com
Conclusion
Retention ponds are essential in managing stormwater runoff effectively. Understanding the depth of a retention pond is crucial for its functionality. Proper maintenance and regular inspections ensure that the pond’s capacity is maximized. By implementing the necessary measures, we can ensure the safety and efficiency of retention ponds in our communities.